The highest demand is within rural off-grid areas, currently underserved, or served by costly fossil fuel-driven pumps. The potential applications include:
• Potable water supply for institutions (traditional niche market for schools and health clinics).
• Community-scale water supply schemes (larger village schemes).
• Livestock water supply (individual or communal).
• Small-scale irrigation (individual farmers or cooperatives).
Solar pumping is most competitive in regions with high solar insolation, which include most of Africa, South America, South Asia, and Southeast Asia. Although these regions all have high radiation, the availability and depth of water resources vary significantly.
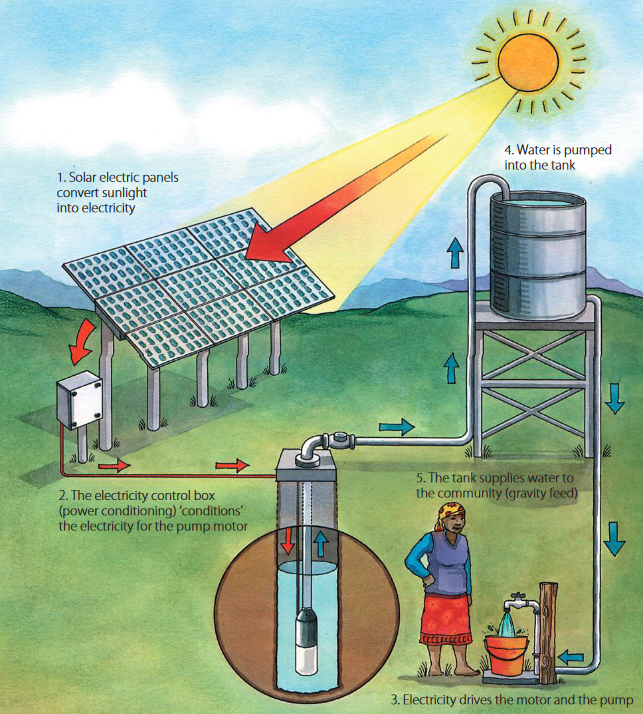
Advantages of solar pumping
- Solar water pump systems consume little to no fuel. By using freely available sunlight, they avoid the constraints of weak or expensive rural fuel supply networks.
- Unlike diesel-based systems (i.e., where a diesel generator powers the pump), solar pumping produces clean energy with zero or much reduced exhaust gases and pollutants.
- Solar pumping systems are durable and reliable. PV panels have a design life of over 20 years, and solar water pumps have few moving parts anf require little maintenance(unlike diesel pumps).
- Solar pumping systems are modular so can be tailored to current power needs and easily expanded by adding PV panels and accessories.
- Properly installed solar systems are safe and low risk due to low system voltage. Adequate protection minimizes fire risk.
Possible disadvantage and mitigation
- Solar pumping systems have high initial capital costs, which can be discouraging. However, component prices are dropping substantially and investment paybacks is quick thanks to vast reductions in fuel usage.
- Water tank storage is preferable to batteries, but still expensive. Hybrid solar/diesel pumping can reduce the need for storage and hence costs.
- Solar pumps still require some servicing, and specialized technicians/providers may be difficult to access in some areas. This is gradually improving.
- Panel theft can be circumvented by sensitizing communities and providing simple antitheft meaures.
- SWP can lead to excessive groundwater extraction because operators face near zero marginal-cost of pimping ground-water.